AlvisNLP data structure
The AlvisNLP data structure is an object shared by all processing steps. It is passed from one processing step to the next. The data structure contains the document structure and content, as well as annotations produced by successive steps. The understanding of the data structure is crucial to to use AlvisNLP since this object allows the steps to communicate with each other.
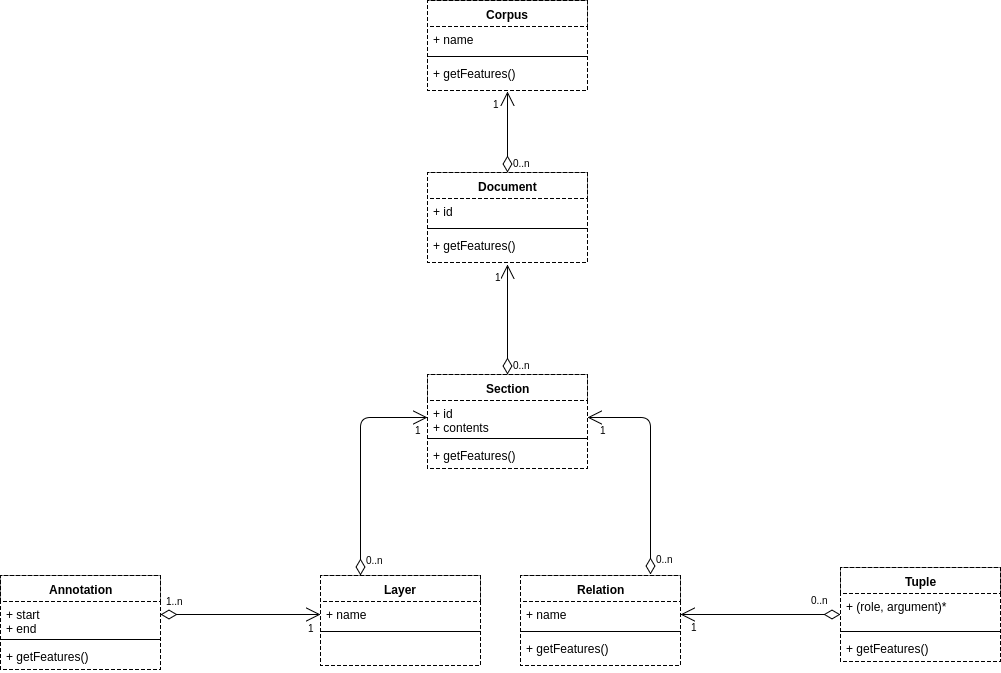
The following figure presents an UML-like specification of the AlvisNLP data structure.
-
Corpus: a
Corpusobject represents a collection of documents. In an AlvisNLP run, the corpus is a unique object passed from module to module. ACorpusobject has features and documents. -
Document: a
Documentobject represents a single document. Each document has an identifier which is unique in the corpus. ADocumentobject has features and sections. -
Section: a
Sectionobject contains a piece of the document’s text contents. Each section has a name, a contents, features, layers, and relations. -
Layer: a
Layerobject is an annotation container. ALayerobject has a name unique in the section. -
Annotation: an
Annotationobject represents a span of text created by a module. Each annotation is included in at least one layer. AnAnnotationobject has a start and end which represent the coordinates of the annotation in the section’s contents, and features. -
Relation: a
Relationobject is a tuple container. ARelationobject has a name unique in the section and features. -
Tuple: a
Tupleobject represents a relation between several elements in the data structure. ATupleobject has several arguments, each argument is an element (Corpus,Document,Section,Relation, but most oftenAnnotationorTuple) accessible through a role name. ATupleobject also has features. -
Features are key-value pairs that contain information on an element type, tag or property. Feature keys are not unique in an element, though when accessing a feature key, the last value is returned.